High Fundamental Frequency (HFF) Monolithic Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Array for the Simultaneous Detection of Pesticides and Antibiotics in Complex Food
Authors: María Calero, Román Fernández, María García, Marisol Juan-Borrás, Isabel Escriche, Antonio Arnau, Ángel Montoya and Yolanda Jiménez.
Journal: Biosensors (2022)
Abstract
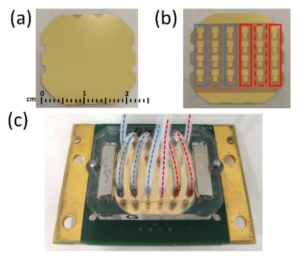
As in the case of the food industry in general, there is a global concern about safety and quality in complex food matrices, such as honey, which is driving the demand for fast, sensitive and affordable analytical techniques across the honey-packaging industry. Although excellent techniques such as liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) are available, these are located in centralized laboratories and are still lacking in speed, simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Here, a new approach is presented where a competitive immunoassay is combined with a novel High Fundamental Frequency Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (HFF-QCMD) array biosensor for the simultaneous detection of antibiotics and pesticides in honey. Concretely, thiabendazole and sulfathiazole residues were monitored in spiked honey samples. Results revealed that HFF-QCMD arrays provide a complementary and reliable tool to LC-MS/MS for the analysis of contaminants in these kinds of complex matrices, while avoiding elaborate sample pre-treatment. The good sensitivity achieved (I50 values in the 70–720 µg/kg range) and the short analysis time (60 min for 24 individual assays), together with the ability for multiple analyte detection (24 sensor array) and its cost-effectiveness, pave the way for the implementation of a fast on-line, in situ routine control of potentially hazardous chemical residues in honey.
You may read the full paper here.
High Fundamental Frequency (HFF) Monolithic Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Array for the Simultaneous Detection of Pesticides and Antibiotics in Complex Food




