Demonstrating a Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCMD) to Enhance the Monitoring and Mechanistic Understanding of Iron Carbonate Crystalline Films
Authors: Igor Efimov, Eftychios Hadjittofis, Mustafa M. Alsalem, and Kyra L. Sedransk Campbell
Journal: Langmuir
Abstract:
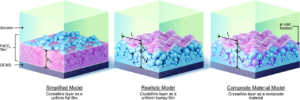 This paper reports the real time monitoring of siderite deposition, on both Au- and Fe-coated surfaces, using the changes in frequency and dissipation of quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCMD). In an iron chloride solution saturated with carbon dioxide, buffered with sodium bicarbonate to pH 6.8, roughly spherical particles of siderite formed within 15 min, which subsequently deposited on the QCMD crystal surface. Imaging of the surface showed a layer formed from particles ca. < 0.5 μm in diameter. Larger particles are clearly deposited on top of the lower layer; these larger particles are >1 μm in diameter. Monitoring of the frequency clearly differentiates the formation of the lower layer from the larger crystals deposited on top at later times. The elastic moduli calculated from QCMD data showed a progressive dissipation increase; the modeling of the solid–liquid interface using a flat approximation resulted in a poor estimation of elastic and storage moduli. Rather, the impedance modeled as a viscoelastic layer in contact with a semi-infinite liquid, where a random bumpy surface with a Gaussian correlator is used, is much more accurate in determining the elastic and storage moduli as losses from the uneven interface are considered. A further step considers that the film is in fact a composite consisting of hard spherical particles of siderite with water in the vacant spaces. This is treated by considering the individual contributions of the phases to the losses measured, thereby further improving the accuracy of the description of the film and the QCMD data. Collectively, this work presents a new framework for the use of QCMD, paired with traditional approaches, to enhance the understanding of crystal deposition and film formation as well as quantify the often evolving mechanical properties.
This paper reports the real time monitoring of siderite deposition, on both Au- and Fe-coated surfaces, using the changes in frequency and dissipation of quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCMD). In an iron chloride solution saturated with carbon dioxide, buffered with sodium bicarbonate to pH 6.8, roughly spherical particles of siderite formed within 15 min, which subsequently deposited on the QCMD crystal surface. Imaging of the surface showed a layer formed from particles ca. < 0.5 μm in diameter. Larger particles are clearly deposited on top of the lower layer; these larger particles are >1 μm in diameter. Monitoring of the frequency clearly differentiates the formation of the lower layer from the larger crystals deposited on top at later times. The elastic moduli calculated from QCMD data showed a progressive dissipation increase; the modeling of the solid–liquid interface using a flat approximation resulted in a poor estimation of elastic and storage moduli. Rather, the impedance modeled as a viscoelastic layer in contact with a semi-infinite liquid, where a random bumpy surface with a Gaussian correlator is used, is much more accurate in determining the elastic and storage moduli as losses from the uneven interface are considered. A further step considers that the film is in fact a composite consisting of hard spherical particles of siderite with water in the vacant spaces. This is treated by considering the individual contributions of the phases to the losses measured, thereby further improving the accuracy of the description of the film and the QCMD data. Collectively, this work presents a new framework for the use of QCMD, paired with traditional approaches, to enhance the understanding of crystal deposition and film formation as well as quantify the often evolving mechanical properties.


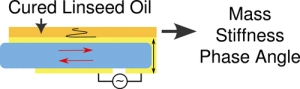 Drying oils such as linseed oil form a polymer network through a complex free-radical polymerization process. We have studied polymerization in this challenging class of polymers using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). The QCM is able to measure the evolution of polymer mass and mechanical properties as the oil transitions from a liquid-like to a solid-like state. Measurements using bulk materials and thin films provide information about the initial polymerization phase as well as the evolution of the mass and mechanical properties over the first two years of cure. The temperature-dependent response of the cured linseed oil films was also measured. These results were combined with previously published results obtained from traditional dynamic mechanical analysis to give a unified picture of the properties of these materials across a very broad temperature range.
Drying oils such as linseed oil form a polymer network through a complex free-radical polymerization process. We have studied polymerization in this challenging class of polymers using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). The QCM is able to measure the evolution of polymer mass and mechanical properties as the oil transitions from a liquid-like to a solid-like state. Measurements using bulk materials and thin films provide information about the initial polymerization phase as well as the evolution of the mass and mechanical properties over the first two years of cure. The temperature-dependent response of the cured linseed oil films was also measured. These results were combined with previously published results obtained from traditional dynamic mechanical analysis to give a unified picture of the properties of these materials across a very broad temperature range.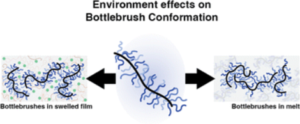 The single-chain physics of bottlebrush polymers plays a key role in their macroscopic properties. Although efforts have been made to understand the behavior of single isolated bottlebrushes, studies on their behavior in crowded, application-relevant environments have been insufficient due to limitations in characterization techniques. Here, we use single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) to study the conformations of individual bottlebrush polymers by direct imaging. Our previous work focused on bottlebrushes in a matrix of linear polymers, where our observations suggested that their behavior was largely influenced by an entropic incompatibility between the bottlebrush side chains and the linear matrix. Instead, here we focus on systems where this effect is reduced: in solvent-swollen polymer materials and in systems entirely composed of bottlebrushes. We measure chain conformations and rigidity using persistence length (lp) as side chain molecular weight (Msc) is varied. Compared to a system of linear polymers, we observe greater flexibility of the backbone in both systems. For bottlebrushes in bottlebrush matrices, we additionally observed a scaling relationship between lp and Msc that more closely follows theoretical predictions. For the more flexible chains in both systems, we reach the edge of our resolution limit and cannot visualize the entire contour of every chain. We bypass this limitation by discussing the aspect ratios of the features within the super-resolution images.
The single-chain physics of bottlebrush polymers plays a key role in their macroscopic properties. Although efforts have been made to understand the behavior of single isolated bottlebrushes, studies on their behavior in crowded, application-relevant environments have been insufficient due to limitations in characterization techniques. Here, we use single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) to study the conformations of individual bottlebrush polymers by direct imaging. Our previous work focused on bottlebrushes in a matrix of linear polymers, where our observations suggested that their behavior was largely influenced by an entropic incompatibility between the bottlebrush side chains and the linear matrix. Instead, here we focus on systems where this effect is reduced: in solvent-swollen polymer materials and in systems entirely composed of bottlebrushes. We measure chain conformations and rigidity using persistence length (lp) as side chain molecular weight (Msc) is varied. Compared to a system of linear polymers, we observe greater flexibility of the backbone in both systems. For bottlebrushes in bottlebrush matrices, we additionally observed a scaling relationship between lp and Msc that more closely follows theoretical predictions. For the more flexible chains in both systems, we reach the edge of our resolution limit and cannot visualize the entire contour of every chain. We bypass this limitation by discussing the aspect ratios of the features within the super-resolution images.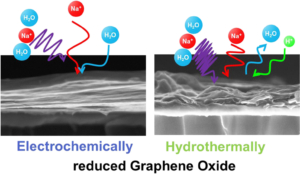 Reduced Graphene Oxide possesses numerous interesting properties, making it one of the most studied materials today. By this way, applications in various fields, including fundamental research, can be found. Nevertheless, the complexity of reduced Graphene Oxide lies in its fabrication process which defines their properties. In this paper, two fabrication methods -electrochemical and hydrothermal reduction of graphene oxide – were compared using physico-chemical and electrogravimetric analysis. Our findings reveal significant morphological differences between the two methods, accompanied by different electrochemical behaviors, when tested in aqueous electrolyte (i.e. 0.5 M Na2SO4). Specifically, electrochemically reduced graphene oxide exclusively involves sodium (whether hydrated or not) in its charge compensation mechanism, whereas hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide also involves proton in sodium sulfate solution.
Reduced Graphene Oxide possesses numerous interesting properties, making it one of the most studied materials today. By this way, applications in various fields, including fundamental research, can be found. Nevertheless, the complexity of reduced Graphene Oxide lies in its fabrication process which defines their properties. In this paper, two fabrication methods -electrochemical and hydrothermal reduction of graphene oxide – were compared using physico-chemical and electrogravimetric analysis. Our findings reveal significant morphological differences between the two methods, accompanied by different electrochemical behaviors, when tested in aqueous electrolyte (i.e. 0.5 M Na2SO4). Specifically, electrochemically reduced graphene oxide exclusively involves sodium (whether hydrated or not) in its charge compensation mechanism, whereas hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide also involves proton in sodium sulfate solution.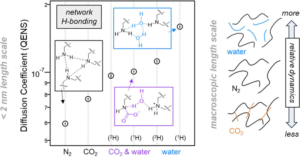 Aminopolymer sorbents are leading candidates for extracting CO2 directly from the atmosphere under ambient conditions. For effective carbon capture, this requires not only that the CO2 actively binds with amine groups of the polymer under low gas concentrations but also that it readily diffuses through the sorbent media to access as many of the amine binding sites as possible. Unfortunately, high reactivity and diffusivity tend to be mutually exclusive properties when it comes to small molecule transport within a polymer, posing a significant materials design challenge. While many reports to date focus on chemical additives or engineering strategies to tackle this trade-off, only a few studies have seriously investigated the underlying chemical and physical properties of the sorbent polymer as a function of its interaction with the relevant sorbate molecules. In this study, we investigate the interplay of polymer-sorbate reactivity and diffusive dynamics of both H2O and CO2 in branched polyethylenimine (PEI) using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS), infrared spectroscopy, gravimetric uptake, and mechanical dissipation measurements as a function of atmospheric dosing conditions. We uncover an intriguing and previously unreported discrepancy in the diffusive dynamics of PEI dosed with CO2 and H2O vapor at the microscopic and macroscopic length scales. At the macroscopic scale, our mechanical dissipation measurements show that while the exposure to H2O vapor alone always plasticizes the dynamics of PEI, the absorption of CO2, either in the presence of H2O or not, leads to a mechanical stiffening of the PEI. Interestingly, this response differs at the microscopic scale where the diffusive dynamics of the H2O- and/or CO2-dosed samples as quantified by QENS are always enhanced relative to the undosed PEI. This dynamic facilitation is greatest in the presence of H2O vapor alone, consistent with H2O strongly plasticizing the dynamics of PEI. However, the simultaneous exposure to both H2O and CO2 leads to a stiffening of the QENS dynamics at the microscopic scale relative to the hydrated state, signifying local interactions between the CO2 and the polymer. Under these conditions, we also observe a greater amount of CO2 absorbed into the PEI film that is simultaneously exposed to both H2O and CO2 as compared to the film exposed to just CO2, further evidencing a complicated three-way interaction between the H2O, CO2, and PEI. These results are discussed in terms of an absorption process that involves the formation of carbamate ions, the generation of ionic cross-link junctions in the PEI, and changes in the local hydration level of the polymer around the ions. To establish the importance of the carbamate ions in this process, we utilize a methylation reaction to modify the PEI and convert all of the primary and secondary amines into tertiary amines that are incapable of forming carbamates. This considerably diminishes the role of hydrogen bonding in the PEI, enhances the microscopic dynamics of the undosed PEI, and results in diffusive dynamics that do not depend heavily on dosing with H2O and/or CO2. The observations reported here provide insights into the design of next-generation aminopolymer sorbents where both reactivity and diffusive dynamics can be optimized.
Aminopolymer sorbents are leading candidates for extracting CO2 directly from the atmosphere under ambient conditions. For effective carbon capture, this requires not only that the CO2 actively binds with amine groups of the polymer under low gas concentrations but also that it readily diffuses through the sorbent media to access as many of the amine binding sites as possible. Unfortunately, high reactivity and diffusivity tend to be mutually exclusive properties when it comes to small molecule transport within a polymer, posing a significant materials design challenge. While many reports to date focus on chemical additives or engineering strategies to tackle this trade-off, only a few studies have seriously investigated the underlying chemical and physical properties of the sorbent polymer as a function of its interaction with the relevant sorbate molecules. In this study, we investigate the interplay of polymer-sorbate reactivity and diffusive dynamics of both H2O and CO2 in branched polyethylenimine (PEI) using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS), infrared spectroscopy, gravimetric uptake, and mechanical dissipation measurements as a function of atmospheric dosing conditions. We uncover an intriguing and previously unreported discrepancy in the diffusive dynamics of PEI dosed with CO2 and H2O vapor at the microscopic and macroscopic length scales. At the macroscopic scale, our mechanical dissipation measurements show that while the exposure to H2O vapor alone always plasticizes the dynamics of PEI, the absorption of CO2, either in the presence of H2O or not, leads to a mechanical stiffening of the PEI. Interestingly, this response differs at the microscopic scale where the diffusive dynamics of the H2O- and/or CO2-dosed samples as quantified by QENS are always enhanced relative to the undosed PEI. This dynamic facilitation is greatest in the presence of H2O vapor alone, consistent with H2O strongly plasticizing the dynamics of PEI. However, the simultaneous exposure to both H2O and CO2 leads to a stiffening of the QENS dynamics at the microscopic scale relative to the hydrated state, signifying local interactions between the CO2 and the polymer. Under these conditions, we also observe a greater amount of CO2 absorbed into the PEI film that is simultaneously exposed to both H2O and CO2 as compared to the film exposed to just CO2, further evidencing a complicated three-way interaction between the H2O, CO2, and PEI. These results are discussed in terms of an absorption process that involves the formation of carbamate ions, the generation of ionic cross-link junctions in the PEI, and changes in the local hydration level of the polymer around the ions. To establish the importance of the carbamate ions in this process, we utilize a methylation reaction to modify the PEI and convert all of the primary and secondary amines into tertiary amines that are incapable of forming carbamates. This considerably diminishes the role of hydrogen bonding in the PEI, enhances the microscopic dynamics of the undosed PEI, and results in diffusive dynamics that do not depend heavily on dosing with H2O and/or CO2. The observations reported here provide insights into the design of next-generation aminopolymer sorbents where both reactivity and diffusive dynamics can be optimized.
