Hydrothermal vs. Electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide: A physico-chemical and quartz crystal microbalance study
Authors: Caroline Keller, Gregory Barbillon, Catherine Debiemme-Chouvy, Ozlem Sel, Hubert Perrot
Journal: Carbon
Abstract
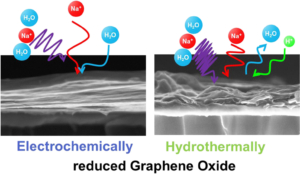 Reduced Graphene Oxide possesses numerous interesting properties, making it one of the most studied materials today. By this way, applications in various fields, including fundamental research, can be found. Nevertheless, the complexity of reduced Graphene Oxide lies in its fabrication process which defines their properties. In this paper, two fabrication methods -electrochemical and hydrothermal reduction of graphene oxide – were compared using physico-chemical and electrogravimetric analysis. Our findings reveal significant morphological differences between the two methods, accompanied by different electrochemical behaviors, when tested in aqueous electrolyte (i.e. 0.5 M Na2SO4). Specifically, electrochemically reduced graphene oxide exclusively involves sodium (whether hydrated or not) in its charge compensation mechanism, whereas hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide also involves proton in sodium sulfate solution.
Reduced Graphene Oxide possesses numerous interesting properties, making it one of the most studied materials today. By this way, applications in various fields, including fundamental research, can be found. Nevertheless, the complexity of reduced Graphene Oxide lies in its fabrication process which defines their properties. In this paper, two fabrication methods -electrochemical and hydrothermal reduction of graphene oxide – were compared using physico-chemical and electrogravimetric analysis. Our findings reveal significant morphological differences between the two methods, accompanied by different electrochemical behaviors, when tested in aqueous electrolyte (i.e. 0.5 M Na2SO4). Specifically, electrochemically reduced graphene oxide exclusively involves sodium (whether hydrated or not) in its charge compensation mechanism, whereas hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide also involves proton in sodium sulfate solution.


