Correlation between the interfacial ion dynamics and charge storage properties of poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) electrodes exhibiting high cycling stability
Authors: El Mahdi Halim, Rezan Demir-Cakan, Hubert Perrot, Mama El Rhazi, Ozlem Sel
Journal: The Journal of Power Sources (2019)
Abstract
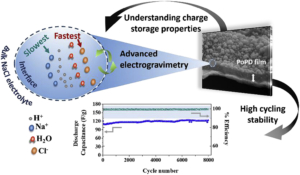
An integrated electrogravimetric study based on electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) unravels the interfacial ion transfer phenomena of the poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) (PoPD) thin film electrodes. Through a methodology coupling QCM with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (ac-electrogravimetry), our work indicates that charge compensation process of PoPD in aqueous electrolytes (in acidified NaCl) occurs with the participation of multiple species, each playing a role at different temporal scales. The PoPD films are tested in a 2 electrode Swagelok cell in which Zn is used as both reference and counter electrodes and exhibit excellent stability over 8000 cycles with a relatively high specific capacitance of about 110 F g−1 at 30 C (0.63 mA cm−2) current density. The high rate capability and the excellent cycling stability of the PoPD electrodes are correlated to the electrolyte composition and the significant role of H+ to the charge compensation process is unravelled, which is made possible with coupled electrogravimetric methods of our study. By determining the interfacial flux dynamics and as well as the relative proportions of species transferred at the electrode/electrolyte interface, our results contribute to the understanding of the charge-discharge process of PoPD polymer, yet underexplored but emerging as a pseudo-capacitive electrode material.
You may read the full paper here.
Correlation between the interfacial ion dynamics and charge storage properties of poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) electrodes exhibiting high cycling stability



