Exploiting the high affinity between cellulose nanofibrils and Aloe vera acemannan to develop elastic, crosslinker-free, all-polysaccharide hydrogels
Authors: Ngoc Huynh, Lukas Fliri, Juan José Valle-Delgado, Monika Österberg
Journal: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
Abstract: Plant-based polymers hold promising prospects thanks to their bioactivity, diversity and versatility but they are currently overshadowed by synthetic and animal-derived materials, especially in biomedical applications. In this study, we developed an entirely plant-based hydrogel with improved mechanical performance based on TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils (TCNFs) and the polysaccharide fraction (AVPF) extracted from Aloe vera L. (Aloe barbadensis Miller). The hydrogel blends exhibited excellent viscoelastic properties, minimal shrinkage and a significant increase in compressive modulus (ranging from 2.7 to 13.2 kPa versus 0.8 kPa in single component hydrogels), suggesting a synergistic effect. In-depth analysis of interaction and morphology of the hydrogels by QCM-D, AFM and SEM imaging showed that the observed synergy was the result of the complementary action between the two components and a uniform spatial distribution of the two networks. TCNFs built the rigid skeleton for the hydrogels, while AVPF physically adsorbed on TCNFs, forming a flexible matrix, allowing for better load transfer and dissipation in both static and dynamic loading, leading to a remarkable increase in moduli that surpassed the mere sum of the two individual components. In addition, the obtained hydrogels also showed little to no perceptible shrinkage after drying, unlike the single-component hydrogels made from the initial materials. These hydrogels offer a sustainable and ethical alternative to animal-derived materials, with great potential in biomedical fields.


 Abstract:
Abstract: 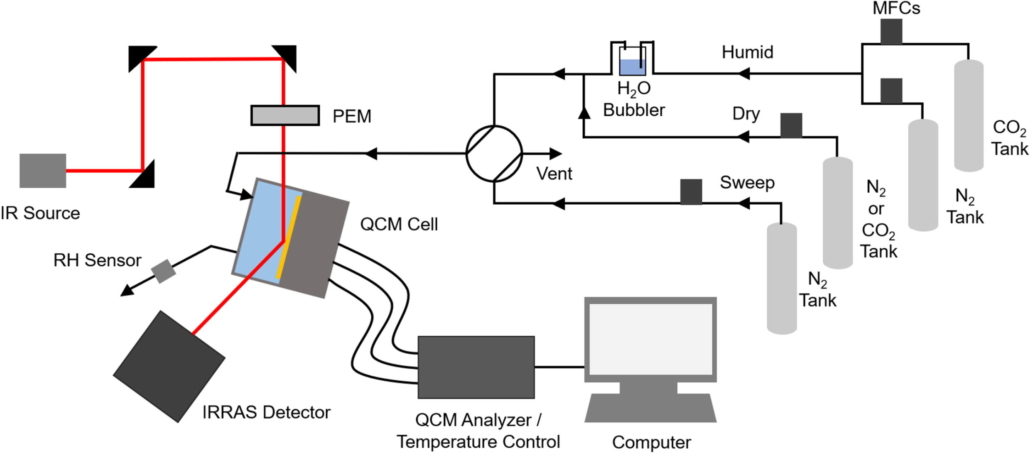 Abstract:
Abstract: 
 Abstract:
Abstract:  Abstract:
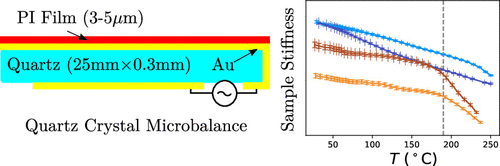
Abstract: 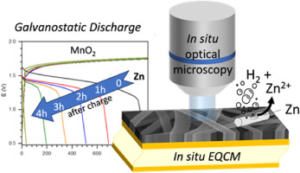 We introduce a novel approach to Zinc-MnO2 battery architecture utilizing a 3D network of carbon nanofibers as both current collector and electrode material, promising enhanced performance and longevity for large-scale energy storage. Employing mild aqueous electrolytes, we address the challenge of managing self-discharge, crucial for short-term energy storage. Advanced coupled characterization techniques, including in-situ EQCM (Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance) and high-resolution optical microscopy, elucidate self-discharge mechanisms across over multiple length scales. Findings reveal that the self-discharge is mainly at the zinc electrode due to concomitant dissolution of Zinc (corrosion) and HER (Hydrogen Evolution Reaction) phenomena. Interestingly, the corrosion current was estimated irrespective of charging protocol and remains consistent, indicating the independence of zinc corrosion kinetics from the length scale. Finally, the morphology of the zinc layer appears to be critical, suggesting that self-discharge is primarily a chemical process. This innovative design strategy offers the potential for high-performance Zinc-MnO2 batteries with extended cycle life to meet the requirements of large-scale energy storage applications.
We introduce a novel approach to Zinc-MnO2 battery architecture utilizing a 3D network of carbon nanofibers as both current collector and electrode material, promising enhanced performance and longevity for large-scale energy storage. Employing mild aqueous electrolytes, we address the challenge of managing self-discharge, crucial for short-term energy storage. Advanced coupled characterization techniques, including in-situ EQCM (Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance) and high-resolution optical microscopy, elucidate self-discharge mechanisms across over multiple length scales. Findings reveal that the self-discharge is mainly at the zinc electrode due to concomitant dissolution of Zinc (corrosion) and HER (Hydrogen Evolution Reaction) phenomena. Interestingly, the corrosion current was estimated irrespective of charging protocol and remains consistent, indicating the independence of zinc corrosion kinetics from the length scale. Finally, the morphology of the zinc layer appears to be critical, suggesting that self-discharge is primarily a chemical process. This innovative design strategy offers the potential for high-performance Zinc-MnO2 batteries with extended cycle life to meet the requirements of large-scale energy storage applications.
