Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring for studying soft matter at interfaces
Authors: Diethelm Johannsmann & Ilya Reviakine
Journal: Nature Reviews Methods Primers
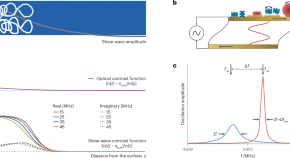 Abstract: Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) probes interfaces by subjecting them to a periodic shear stress exerted by an acoustic resonator. The changes in the resonance frequency, Δf, and the half-width at half-maximum of the resonance, ΔΓ (closely related to the changes in the dissipation, ΔD), measured with the QCM-D are proportional to the in-phase and out-of-phase components of the area-averaged transverse stress at the resonator surface, respectively. Amounts, organization and properties of soft matter at an interface between the resonator and a liquid or a gas are derived from the measurements of Δf and ΔΓ on multiple overtones at megahertz frequencies. The properties include viscoelasticity and stress relaxation dynamics on the timescale of the oscillation period. This Primer offers guidelines on instrument design, experimental procedures and data analysis for interpreting frequency and bandwidth changes in terms of structure and dynamics of the sample. There is a focus on recent progress in the analysis of the acoustic ratio, ΔΓ/(−Δf), and numerical methods of modelling. Limitations of the existing approaches for data analysis are discussed. Challenges and possible future developments are formulated in an outlook.
Abstract: Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) probes interfaces by subjecting them to a periodic shear stress exerted by an acoustic resonator. The changes in the resonance frequency, Δf, and the half-width at half-maximum of the resonance, ΔΓ (closely related to the changes in the dissipation, ΔD), measured with the QCM-D are proportional to the in-phase and out-of-phase components of the area-averaged transverse stress at the resonator surface, respectively. Amounts, organization and properties of soft matter at an interface between the resonator and a liquid or a gas are derived from the measurements of Δf and ΔΓ on multiple overtones at megahertz frequencies. The properties include viscoelasticity and stress relaxation dynamics on the timescale of the oscillation period. This Primer offers guidelines on instrument design, experimental procedures and data analysis for interpreting frequency and bandwidth changes in terms of structure and dynamics of the sample. There is a focus on recent progress in the analysis of the acoustic ratio, ΔΓ/(−Δf), and numerical methods of modelling. Limitations of the existing approaches for data analysis are discussed. Challenges and possible future developments are formulated in an outlook.
The full article can be accessed here.