Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance to Monitor the Curing of Drying Oils
Authors: Gwen dePolo, Arnaud Lesaine, Marco Faustini, Lucie Laporte, Côme Thillaye du Boullay, Étienne Barthel, Joen Hermans, Piet D. Iedema, Laurence de Viguerie, and Kenneth R. Shull
Journal: Anal. Chem
Abstract:
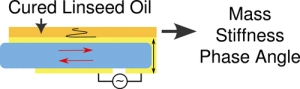 Drying oils such as linseed oil form a polymer network through a complex free-radical polymerization process. We have studied polymerization in this challenging class of polymers using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). The QCM is able to measure the evolution of polymer mass and mechanical properties as the oil transitions from a liquid-like to a solid-like state. Measurements using bulk materials and thin films provide information about the initial polymerization phase as well as the evolution of the mass and mechanical properties over the first two years of cure. The temperature-dependent response of the cured linseed oil films was also measured. These results were combined with previously published results obtained from traditional dynamic mechanical analysis to give a unified picture of the properties of these materials across a very broad temperature range.
Drying oils such as linseed oil form a polymer network through a complex free-radical polymerization process. We have studied polymerization in this challenging class of polymers using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). The QCM is able to measure the evolution of polymer mass and mechanical properties as the oil transitions from a liquid-like to a solid-like state. Measurements using bulk materials and thin films provide information about the initial polymerization phase as well as the evolution of the mass and mechanical properties over the first two years of cure. The temperature-dependent response of the cured linseed oil films was also measured. These results were combined with previously published results obtained from traditional dynamic mechanical analysis to give a unified picture of the properties of these materials across a very broad temperature range.