Demonstrating a Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCMD) to Enhance the Monitoring and Mechanistic Understanding of Iron Carbonate Crystalline Films
Authors: Igor Efimov, Eftychios Hadjittofis, Mustafa M. Alsalem, and Kyra L. Sedransk Campbell
Journal: Langmuir
Abstract:
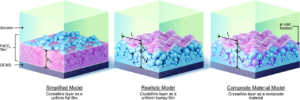 This paper reports the real time monitoring of siderite deposition, on both Au- and Fe-coated surfaces, using the changes in frequency and dissipation of quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCMD). In an iron chloride solution saturated with carbon dioxide, buffered with sodium bicarbonate to pH 6.8, roughly spherical particles of siderite formed within 15 min, which subsequently deposited on the QCMD crystal surface. Imaging of the surface showed a layer formed from particles ca. < 0.5 μm in diameter. Larger particles are clearly deposited on top of the lower layer; these larger particles are >1 μm in diameter. Monitoring of the frequency clearly differentiates the formation of the lower layer from the larger crystals deposited on top at later times. The elastic moduli calculated from QCMD data showed a progressive dissipation increase; the modeling of the solid–liquid interface using a flat approximation resulted in a poor estimation of elastic and storage moduli. Rather, the impedance modeled as a viscoelastic layer in contact with a semi-infinite liquid, where a random bumpy surface with a Gaussian correlator is used, is much more accurate in determining the elastic and storage moduli as losses from the uneven interface are considered. A further step considers that the film is in fact a composite consisting of hard spherical particles of siderite with water in the vacant spaces. This is treated by considering the individual contributions of the phases to the losses measured, thereby further improving the accuracy of the description of the film and the QCMD data. Collectively, this work presents a new framework for the use of QCMD, paired with traditional approaches, to enhance the understanding of crystal deposition and film formation as well as quantify the often evolving mechanical properties.
This paper reports the real time monitoring of siderite deposition, on both Au- and Fe-coated surfaces, using the changes in frequency and dissipation of quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCMD). In an iron chloride solution saturated with carbon dioxide, buffered with sodium bicarbonate to pH 6.8, roughly spherical particles of siderite formed within 15 min, which subsequently deposited on the QCMD crystal surface. Imaging of the surface showed a layer formed from particles ca. < 0.5 μm in diameter. Larger particles are clearly deposited on top of the lower layer; these larger particles are >1 μm in diameter. Monitoring of the frequency clearly differentiates the formation of the lower layer from the larger crystals deposited on top at later times. The elastic moduli calculated from QCMD data showed a progressive dissipation increase; the modeling of the solid–liquid interface using a flat approximation resulted in a poor estimation of elastic and storage moduli. Rather, the impedance modeled as a viscoelastic layer in contact with a semi-infinite liquid, where a random bumpy surface with a Gaussian correlator is used, is much more accurate in determining the elastic and storage moduli as losses from the uneven interface are considered. A further step considers that the film is in fact a composite consisting of hard spherical particles of siderite with water in the vacant spaces. This is treated by considering the individual contributions of the phases to the losses measured, thereby further improving the accuracy of the description of the film and the QCMD data. Collectively, this work presents a new framework for the use of QCMD, paired with traditional approaches, to enhance the understanding of crystal deposition and film formation as well as quantify the often evolving mechanical properties.




