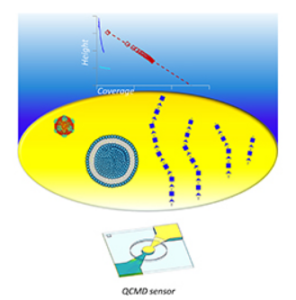
The Frequency‐Domain Lattice Boltzmann Method (FreqD‐LBM): A Versatile Tool to Predict the QCM Response Induced by Structured Samples
Authors: Diethelm Johannsmann, Paul Häusner, Arne Langhoff, Christian Leppin, Ilya Reviakine, Viktor Vanoppen
Journal: Advanced Theory and Simulations
Abstract: 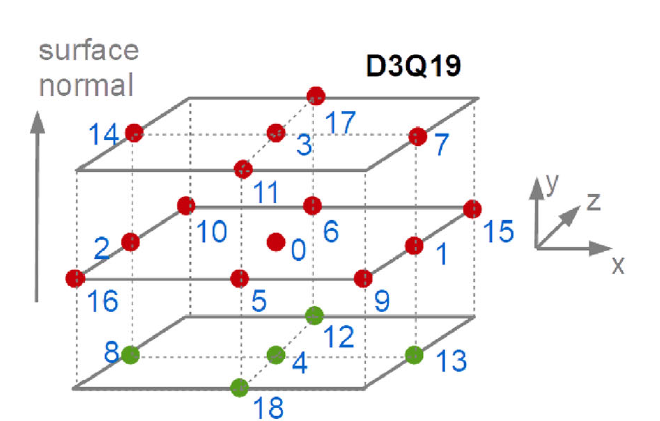 The quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) is routinely used to investigate structured samples. Here, a simulation technique is described, that predicts the shifts of frequency and half bandwidth, Δfn and ΔΓn, of a quartz resonator operating on different overtone orders, n, induced by structured samples in contact with the resonator surface in liquid. The technique, abbreviated as FreqD-LBM, solves the Stokes equation in the frequency domain. The solution provides the complex amplitude of the area-averaged tangential stress at the resonator surface, from which Δfn and ΔΓn are derived. Because the dynamical variables are complex amplitudes, the viscosity can be complex, as well. The technique naturally covers viscoelasticity. Limitations are linked to the grid resolution and to problems at large viscosity. Validation steps include viscoelastic films, rough surfaces, an oscillating cylinder in a viscous medium, and a free-floating sphere above the resonator. Application examples are soft adsorbed particles, stiff adsorbed particles, and a large, immobile spherical cap above the resonator, which allows to study the high-frequency properties of the material in the gap. FreqDLBM runs on an office PC and does not require expert knowledge of numerical techniques. It is accessible to an experimentalist.
The quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) is routinely used to investigate structured samples. Here, a simulation technique is described, that predicts the shifts of frequency and half bandwidth, Δfn and ΔΓn, of a quartz resonator operating on different overtone orders, n, induced by structured samples in contact with the resonator surface in liquid. The technique, abbreviated as FreqD-LBM, solves the Stokes equation in the frequency domain. The solution provides the complex amplitude of the area-averaged tangential stress at the resonator surface, from which Δfn and ΔΓn are derived. Because the dynamical variables are complex amplitudes, the viscosity can be complex, as well. The technique naturally covers viscoelasticity. Limitations are linked to the grid resolution and to problems at large viscosity. Validation steps include viscoelastic films, rough surfaces, an oscillating cylinder in a viscous medium, and a free-floating sphere above the resonator. Application examples are soft adsorbed particles, stiff adsorbed particles, and a large, immobile spherical cap above the resonator, which allows to study the high-frequency properties of the material in the gap. FreqDLBM runs on an office PC and does not require expert knowledge of numerical techniques. It is accessible to an experimentalist.


 Abstract:
Abstract: 
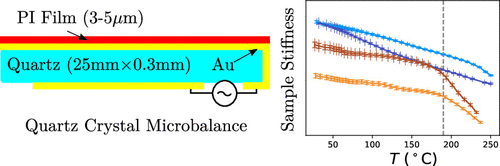
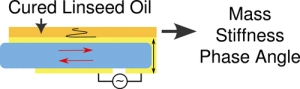 Drying oils such as linseed oil form a polymer network through a complex free-radical polymerization process. We have studied polymerization in this challenging class of polymers using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). The QCM is able to measure the evolution of polymer mass and mechanical properties as the oil transitions from a liquid-like to a solid-like state. Measurements using bulk materials and thin films provide information about the initial polymerization phase as well as the evolution of the mass and mechanical properties over the first two years of cure. The temperature-dependent response of the cured linseed oil films was also measured. These results were combined with previously published results obtained from traditional dynamic mechanical analysis to give a unified picture of the properties of these materials across a very broad temperature range.
Drying oils such as linseed oil form a polymer network through a complex free-radical polymerization process. We have studied polymerization in this challenging class of polymers using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). The QCM is able to measure the evolution of polymer mass and mechanical properties as the oil transitions from a liquid-like to a solid-like state. Measurements using bulk materials and thin films provide information about the initial polymerization phase as well as the evolution of the mass and mechanical properties over the first two years of cure. The temperature-dependent response of the cured linseed oil films was also measured. These results were combined with previously published results obtained from traditional dynamic mechanical analysis to give a unified picture of the properties of these materials across a very broad temperature range.