Immobilization of DNA probes on a high frequency piezoelectric biosensor
Authors: Camilo Ortiz-Monsalve, Jorge Mario Guerra-González & Marisol Jaramillo-Grajales
Journal: DYNA, 2020
Categoría publications
Authors: Camilo Ortiz-Monsalve, Jorge Mario Guerra-González & Marisol Jaramillo-Grajales
Journal: DYNA, 2020
Authors: Lourdes Cervera‐Chiner, Carmen March, Antonio Arnau, Yolanda Jiménez
Ángel Montoya
Journal: Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020
Authors: Elise Duquesne, Stephanie Betelu, Cyrille Bazin, Alain Seron,Ioannis Ignatiadis, Hubert Perrot, Ozlem Sel, Catherine Debiemme-Chouvy
Journal: The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020
Authors: S. Gogoi, S. Kalita, R. Hazarika, P. Puzari
Journal: Electrochimica Acta, 2020
Authors:
Pierre Lemaire, Ozlem Sel, Daniel Alves Dalla Corte, Antonella Iadecola, Hubert Perrot, Jean-Marie Tarascon
Journal: ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019
Authors: Frederick Meyer, Arne Langhoff, Antonio Arnau, Diethelm Johannsmann, and Ilya Reviakine
Journal: Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019
Authors: Liyuan Liu, Yih-Chyng Wu, Patrick Rozier, Pierre-Louis Taberna, and Patrice Simon
Journal: Research, vol. 2019
Authors: Wesley B. S. Machini Nuno V. Marques Prof. Dr. Ana Maria Oliveira‐Brett
Journal: ChemElectroChem 2019
Authors: Kyoung-Sik Choi, Ji Woong Han, Min Hyung Kim, Miyeon Yoon, Yang-Rae Kim, In Tae Kim
Journal: Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2019
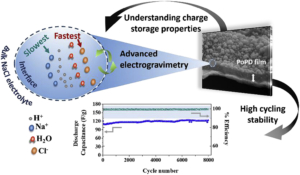
Correlation between the interfacial ion dynamics and charge storage properties of poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) electrodes exhibiting high cycling stability
Authors: El Mahdi Halim, Rezan Demir-Cakan, Hubert Perrot, Mama El Rhazi, Ozlem Sel
Journal: The Journal of Power Sources (2019)
Abstract
An integrated electrogravimetric study based on electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) unravels the interfacial ion transfer phenomena of the poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) (PoPD) thin film electrodes. Through a methodology coupling QCM with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (ac-electrogravimetry), our work indicates that charge compensation process of PoPD in aqueous electrolytes (in acidified NaCl) occurs with the participation of multiple species, each playing a role at different temporal scales. The PoPD films are tested in a 2 electrode Swagelok cell in which Zn is used as both reference and counter electrodes and exhibit excellent stability over 8000 cycles with a relatively high specific capacitance of about 110 F g−1 at 30 C (0.63 mA cm−2) current density. The high rate capability and the excellent cycling stability of the PoPD electrodes are correlated to the electrolyte composition and the significant role of H+ to the charge compensation process is unravelled, which is made possible with coupled electrogravimetric methods of our study. By determining the interfacial flux dynamics and as well as the relative proportions of species transferred at the electrode/electrolyte interface, our results contribute to the understanding of the charge-discharge process of PoPD polymer, yet underexplored but emerging as a pseudo-capacitive electrode material.
You may read the full paper here.
Correlation between the interfacial ion dynamics and charge storage properties of poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) electrodes exhibiting high cycling stability

From this panel the user will be able to configure the cookies that the website can install in their browser, except for the technical or functional cookies that are necessary for browsing and using the different options or services that are offered.
The selected cookies indicate that the user authorises the installation in their browser and the processing of data under the conditions stated in the Cookie Policy.
The user can check or uncheck as they wish to accept or reject the installation of cookies.
COOKIES CONTROLLED BY THE EDITOR
| Analytics | ||||
| Property | Cookie | Purpose | Term | |
| awsensors.com | _ga | ID used to identify users | in 2 years | |
| awsensors.com | _gat | Used to monitor number of Google Analytics server requests when using Google Tag Manager | Sesión | |
| awsensors.com | _gid | ID used to identify users for 24 hours after last activity | in 20 hours | |
| Marketing | ||||
| Property | Cookie | Purpose | Term | |
| google.com | NID | This cookies is used to collect website statistics and track conversion rates and Google ad personalisation | in 7 months |
| HOW TO MANAGE COOKIES FROM YOUR BROWSER | ||
| Delete cookies from your device | Cookies that are already on a device can be deleted by clearing the browser history, thus deleting the cookies from all websites visited.
However, some of the saved information (e.g. login data or website preferences) may also be lost. |
|
| Manage site specific cookies | For more precise control of site specific cookies, users can adjust their privacy settings and cookies in their browser. | |
| Blocking cookies | While most modern browsers can be configured to prevent cookies from being installed on a device, this may require the manual adjustment of certain preferences each time a site or page is visited. In addition, some services and features may not work properly (for example, profile logins). | |
| HOW TO DELETE COOKIES FROM MOST COMMON BROWSERS | ||
| Chrome | http://support.google.com/chrome/answer/95647?hl=es | |
| Internet Explorer. Version 11 | https://support.microsoft.com/es-es/help/278835/how-to-delete-cookie-files-in-internet-explorer | |
| Firefox. Version 65.0.1 | https://www.mozilla.org/es-ES/privacy/websites/#cookies | |
| Safari Version 5.1 | https://support.apple.com/es-es/guide/safari/sfri11471/mac | |
| Opera | https://help.opera.com/en/latest/security-and-privacy/#clearBrowsingData | |
Desde este panel podrá configurar las cookies que el sitio web puede instalar en su navegador, excepto las cookies técnicas o funcionales que son necesarias para la navegación y la utilización de las diferentes opciones o servicios que se ofrecen.
Las cookies seleccionadas indican que el usuario autoriza la instalación en su navegador y el tratamiento de datos bajo las condiciones reflejadas en la Política de cookies.
El usuario puede marcar o desmarcar el selector según se desee aceptar o rechazar la instalación de cookies.
COOKIES CONTROLADAS POR EL EDITOR
| Analíticas | ||||
| Propiedad | Cookie | Finalidad | Plazo | |
| awsensors.com | _ga | ID utiliza para identificar a los usuarios | en 2 años | |
| awsensors.com | _gat | Se utiliza para monitorizar el número de peticiones al servidor de Google Analytics cuando se utiliza el Administrador de etiquetas Google | Sesión | |
| awsensors.com | _gid | ID utiliza para identificar a los usuarios durante 24 horas después de la última actividad | en 20 horas | |
| Publicitarias | ||||
| Propiedad | Cookie | Finalidad | Plazo | |
| google.com | NID | Estas cookies se utilizan para recopilar estadísticas del sitio web y rastrear las tasas de conversión y la personalización de anuncios de Google | en 7 meses |
| CÓMO GESTIONAR LAS COOKIES DESDE EL NAVEGADOR | ||
| Eliminar las cookies del dispositivo | Las cookies que ya están en un dispositivo se pueden eliminar borrando el historial del navegador, con lo que se suprimen las cookies de todos los sitios web visitados. Sin embargo, también se puede perder parte de la información guardada (por ejemplo, los datos de inicio de sesión o las preferencias de sitio web). | |
| Gestionar las cookies específicas del sitio | Para tener un control más preciso de las cookies específicas de cada sitio, los usuarios pueden ajustar su configuración de privacidad y cookies en el navegador. | |
| Bloquear las cookies | Aunque la mayoría de los navegadores modernos se pueden configurar para evitar que se instalen cookies en los dispositivos, eso puede obligar al ajuste manual de determinadas preferencias cada vez que se visite un sitio o página. Además, algunos servicios y características pueden no funcionar correctamente (por ejemplo, los inicios de sesión con perfil). | |
| CÓMO ELIMINAR LAS COOKIES DE LOS NAVEGADORES MÁS COMUNES | ||
| Chrome | http://support.google.com/chrome/answer/95647?hl=es | |
| Internet Explorer. Versión 11 | https://support.microsoft.com/es-es/help/278835/how-to-delete-cookie-files-in-internet-explorer | |
| Firefox. Versión 65.0.1 | https://www.mozilla.org/es-ES/privacy/websites/#cookies | |
| Safari Versión 5.1 | https://support.apple.com/es-es/guide/safari/sfri11471/mac | |
| Opera | https://help.opera.com/en/latest/security-and-privacy/#clearBrowsingData | |
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
Las cookies estrictamente necesarias tiene que activarse siempre para que podamos guardar tus preferencias de ajustes de cookies.
Básicamente la web no funcionará bien si no las activas.
Estas cookies son:
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Si desactivas esta cookie no podremos guardar tus preferencias. Esto significa que cada vez que visites esta web tendrás que activar o desactivar las cookies de nuevo.
Third-party services are beyond the control of the editor. Suppliers may at any time modify their service conditions, the purpose and use of cookies, etc.
External suppliers of this website:
| Editor | Privacy Policy |
| Google Analytics | https://privacy.google.com/take-control.html |
| https://privacy.google.com/take-control.html | |
| PHP.net | https://www.php.net/privacy.php |
| Wordpress | https://wordpress.org/about/privacy/cookies/ |
COOKIES CONTROLLED BY THE EDITOR
| Analytics | ||||
| Property | Cookie | Purpose | Term | |
| awsensors.com | _ga | ID used to identify users | in 2 years | |
| awsensors.com | _gat | Used to monitor number of Google Analytics server requests when using Google Tag Manager | Sesión | |
| awsensors.com | _gid | ID used to identify users for 24 hours after last activity | in 20 hours | |
| Marketing | ||||
| Property | Cookie | Purpose | Term | |
| google.com | NID | This cookies is used to collect website statistics and track conversion rates and Google ad personalisation | in 7 months |
COOKIES DE TERCEROS
COOKIES CONTROLADAS POR EL EDITOR
Los servicios de terceros son ajenos al control del editor. Los proveedores pueden modificar en todo momento sus condiciones de servicio, finalidad y utilización de las cookies, etc.
| Editor | Política de privacidad |
| Google Analytics | https://privacy.google.com/take-control.html |
| https://privacy.google.com/take-control.html | |
| PHP.net | https://www.php.net/privacy.php |
| Wordpress | https://wordpress.org/about/privacy/cookies/ |
Proveedores externos de este sitio web:
| Analíticas | ||||
| Propiedad | Cookie | Finalidad | Plazo | |
| awsensors.com | _ga | ID utiliza para identificar a los usuarios | en 2 años | |
| awsensors.com | _gat | Se utiliza para monitorizar el número de peticiones al servidor de Google Analytics cuando se utiliza el Administrador de etiquetas Google | Sesión | |
| awsensors.com | _gid | ID utiliza para identificar a los usuarios durante 24 horas después de la última actividad | en 20 horas | |
| Publicitarias | ||||
| Propiedad | Cookie | Finalidad | Plazo | |
| google.com | NID | Estas cookies se utilizan para recopilar estadísticas del sitio web y rastrear las tasas de conversión y la personalización de anuncios de Google | en 7 meses |
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!
¡Por favor, activa primero las cookies estrictamente necesarias para que podamos guardar tus preferencias!
More information about our Cookie Policy
Más información sobre nuestra política de cookies aquí
