July 27th 2017
Swedish and Spanish companies invested in AWSensors seeing a growth opportunity.
AWSensors raised 1M€ investment round to strengthen its position in scientific market and enter the healthcare tech market, one of the most competitive markets. The company though has convinced Swedish and Spanish investors that the potential payoff is worth the risk.
Firms entering into the investment round were BAble Capital, a venture capital firm that aims to invest in technology-based companies from Spanish universities and research centers, and Tech Transfer UPV, a venture capital firm created specifically to transfer technology developed at the Spanish university, Polytechnic University of Valencia. But also a consortium of Swedish companies invested in AWSensors seeing a growth opportunity. Other Spanish companies like PolymerChar, Keodes or Citrosol are also among the shareholders.

AWSensors, led by Prof. Antonio Arnau, expects to speed up innovation processes to launch new scientific equipments to meet demand from scientists and industry R&D but also to develop cutting-edge healthcare technology to be applied in personalized medicine.
The aim of these new developments is to get a blood test meant to catch cancer when it’s most treatable, before patients show symptoms, by detecting fragments of DNA shed by tumors. A new liquid biopsy system will allow for detection of this circulating DNA and its mutations and will be an essential equipment to help doctors diagnose, monitor and treat cancer patients in a personalized way.
To hit that goal, AWSensors got another 1M€ from European Comission through two H2020 European projects:
- LiqBiopSens project, that is coordinated by AWSensors and developed together with companies and institutions from Spain, Belgium, UK and Greece.
- Catch-u-DNA project, which is carried out with partners from Germany, France, Israel, Greece and Spain.
These projects as a whole were funded with 5.7M€ by European Comission.
AWSENSORS CONSIGUE UNA INVERSIÓN DE 1 MILLÓN DE EUROS
Nuevos inversores de Suecia y España entran en el accionariado de la compañía
AWSensors ha conseguido despertar el interés de inversores nacionales e internacionales y realizar una ronda de 1 millón de euros. En la operación de inversión han participado BeAble Capital, sociedad gestora que tiene como objetivo invertir en empresas de base tecnológica con origen en universidades y centros de investigación españoles, y Tech Transfer UPV, fondo creado específicamente para trasladar al mercado tecnología desarrollada en la Universidad Politécnica de Valencia. Pero también un consorcio de empresas tecnológicas suecas ha apostado fuerte por entrar como inversor en AWSensors. Además, empresas valencianas como PolymerChar, Keodes o Citrosol están también entre los accionistas.
Esta inversión permitirá a AWSensors consolidarse en el mercado científico internacional donde comercializa una nueva tecnología patentada de sensores para análisis de interacciones moleculares en tiempo real que utilizan investigadores de Europa, Estados Unidos y Asia en los campos de ciencias de la vida y nuevos materiales.
La compañía, liderada por el Prof. Antonio Arnau, espera invertir en nueva infraestructura de fabricación y captar nuevo talento para su plantilla. El objetivo es acelerar el proceso de innovación para sacar al mercado nuevos equipos con mayor productividad y automatización e iniciar nuevos desarrollos para el mercado de salud, ya que la tecnología de AWSensors podrá ser aplicada en medicina personalizada.
Uno de los desarrollos previstos para el mercado sanitario es un equipo para la detección precoz de cáncer colorrectal y su monitorización sin necesidad de entrar al quirófano para realizar una biopsia del tumor. Servirá con un análisis de sangre cuyos resultados se podrían obtener en una hora. La detección en este caso se basa en el ADN que libera el tumor en el organismo. El nuevo sistema permitirá detectar ese ADN circulante y las mutaciones que sufre asociadas al cáncer. Este análisis, denominado biopsia líquida, permitirá un control sencillo del paciente y facilitará por tanto la adaptación del tratamiento de forma personalizada.

Este nuevo equipo se está desarrollando junto a otras empresas e instituciones de España, Bélgica, Reino Unido y Grecia dentro del proyecto LiqBiopSens financiado por la Comisión Europea dentro del programa H2020. Un proyecto que ha inyectado medio millón de euros a AWSensors.
Paralelamente a este desarrollo, AWSensors participa en otro proyecto europeo, Catch-u-DNA que investiga una nueva técnica para mejorar la sensibilidad de la tecnología en la detección del ADN circulante. Este proyecto, que se realiza con socios de Alemania, Francia, Israel, Grecia y España, ha supuesto el ingreso de medio millón de euros más en la compañía.
En total, la Comisión Europea ha dotado con 5’7 millones de euros a estos dos proyectos de investigación cuyos resultados impulsarán el crecimiento de AWSensor



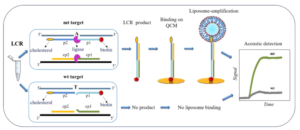
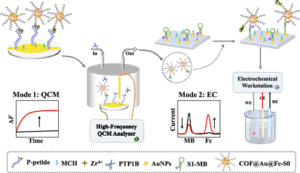 The abnormal expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) is highly related to several serious human diseases. Therefore, an accurate PTP1B activity assay is beneficial to the diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. In this study, a dual-mode biosensing platform that enabled the sensitive and accurate assay of PTP1B activity was constructed based on the high-frequency (100 MHz) quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) and dual-signaling electrochemical (EC) ratiometric strategy. Covalent–organic framework@gold nanoparticles@ferrocene@single-strand DNA (COF@Au@Fc-S0) was introduced onto the QCM Au chip via the chelation between Zr4+ and phosphate groups (phosphate group of the phosphopeptide (P-peptide) on the QCM Au chip and the phosphate group of thiol-labeled single-stranded DNA (S0) on COF@Au@Fc-S0) and used as a signal reporter. When PTP1B was present, the dephosphorylation of the P-peptide led to the release of COF@Au@Fc-S0 from the QCM Au chip, resulting in an increase in the frequency of the QCM. Meanwhile, the released COF@Au@Fc-S0 hybridized with thiol/methylene blue (MB)-labeled hairpin DNA (S1-MB) on the Au NPs-modified indium–tin oxide (ITO) electrode. This caused MB to be far away from the electrode surface and Fc to be close to the electrode, leading to a decrease in the oxidation peak current of MB and an increase in the oxidation peak current of Fc. Thus, PTP1B-induced dephosphorylation of the P-peptide was monitored in real time by QCM, and PTP1B activity was detected sensitively and reliably using this innovative QCM-EC dual-mode sensing platform with an ultralow detection limit. This platform is anticipated to serve as a robust tool for the analysis of protein phosphatase activity and the discovery of drugs targeting protein phosphatase.
The abnormal expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) is highly related to several serious human diseases. Therefore, an accurate PTP1B activity assay is beneficial to the diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. In this study, a dual-mode biosensing platform that enabled the sensitive and accurate assay of PTP1B activity was constructed based on the high-frequency (100 MHz) quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) and dual-signaling electrochemical (EC) ratiometric strategy. Covalent–organic framework@gold nanoparticles@ferrocene@single-strand DNA (COF@Au@Fc-S0) was introduced onto the QCM Au chip via the chelation between Zr4+ and phosphate groups (phosphate group of the phosphopeptide (P-peptide) on the QCM Au chip and the phosphate group of thiol-labeled single-stranded DNA (S0) on COF@Au@Fc-S0) and used as a signal reporter. When PTP1B was present, the dephosphorylation of the P-peptide led to the release of COF@Au@Fc-S0 from the QCM Au chip, resulting in an increase in the frequency of the QCM. Meanwhile, the released COF@Au@Fc-S0 hybridized with thiol/methylene blue (MB)-labeled hairpin DNA (S1-MB) on the Au NPs-modified indium–tin oxide (ITO) electrode. This caused MB to be far away from the electrode surface and Fc to be close to the electrode, leading to a decrease in the oxidation peak current of MB and an increase in the oxidation peak current of Fc. Thus, PTP1B-induced dephosphorylation of the P-peptide was monitored in real time by QCM, and PTP1B activity was detected sensitively and reliably using this innovative QCM-EC dual-mode sensing platform with an ultralow detection limit. This platform is anticipated to serve as a robust tool for the analysis of protein phosphatase activity and the discovery of drugs targeting protein phosphatase.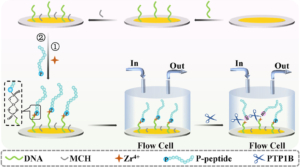 The misregulation of protein phosphatases is a key factor in the development of many human diseases, notably cancers. Here, based on a 100 MHz quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) biosensing platform, the dephosphorylation process of phosphopeptide (P-peptide) caused by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) was monitored in real time for the first time and PTP1B activity was assayed rapidly and sensitively. The QCM chip, coated with a gold (Au) film, was used to immobilized thiol-labeled single-stranded 5′-phosphate-DNAs (P-DNA) through Au–S bond. The P-peptide, specific to PTP1B, was then connected to the P-DNA via chelation between Zr4+ and phosphate groups. When PTP1B was injected into the QCM flow cell where the P-peptide/Zr4+/MCH/P-DNA/Au chip was placed, the P-peptide was dephosphorylated and released from the Au chip surface, resulting in an increase in the frequency of the QCM Au chip. This allowed the real-time monitoring of the P-peptide dephosphorylation process and sensitive detection of PTP1B activity within 6 min with a linear detection range of 0.01–100 pM and a detection limit of 0.008 pM. In addition, the maximum inhibitory ratios of inhibitors were evaluated using this proposed 100 MHz QCM biosensor. The developed 100 MHz QCM biosensing platform shows immense potential for early diagnosis of diseases related to protein phosphatases and the development of drugs targeting protein phosphatases.
The misregulation of protein phosphatases is a key factor in the development of many human diseases, notably cancers. Here, based on a 100 MHz quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) biosensing platform, the dephosphorylation process of phosphopeptide (P-peptide) caused by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) was monitored in real time for the first time and PTP1B activity was assayed rapidly and sensitively. The QCM chip, coated with a gold (Au) film, was used to immobilized thiol-labeled single-stranded 5′-phosphate-DNAs (P-DNA) through Au–S bond. The P-peptide, specific to PTP1B, was then connected to the P-DNA via chelation between Zr4+ and phosphate groups. When PTP1B was injected into the QCM flow cell where the P-peptide/Zr4+/MCH/P-DNA/Au chip was placed, the P-peptide was dephosphorylated and released from the Au chip surface, resulting in an increase in the frequency of the QCM Au chip. This allowed the real-time monitoring of the P-peptide dephosphorylation process and sensitive detection of PTP1B activity within 6 min with a linear detection range of 0.01–100 pM and a detection limit of 0.008 pM. In addition, the maximum inhibitory ratios of inhibitors were evaluated using this proposed 100 MHz QCM biosensor. The developed 100 MHz QCM biosensing platform shows immense potential for early diagnosis of diseases related to protein phosphatases and the development of drugs targeting protein phosphatases.