Portable Surface Acoustic Wave device platform coupled with a paper-based capillary fluidics for real-time biosensing applications
Authors: Angelos Ntimtsas and Electra Gizeli
Journal: Chemical Society Sensors and Actuators A: Physical
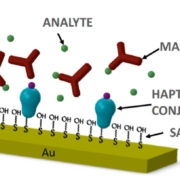
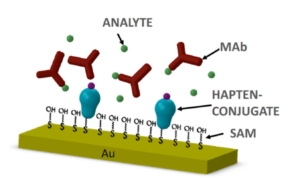
Abstract: Surface acoustic wave (SAW) sensors have emerged as prominent real-time, label-free biosensors with diverse applications in immunoassays and nucleic acid detection. However, widespread adoption in diagnostics has been impeded by challenges such as miniaturization of instrumentation, microfluidics fabrication and high attenuation in liquid environments. In this study we address these limitations by presenting a portable platform capable of real-time monitoring of a SAW microarray chip comprising up to four sensing channels, combined with a novel paper-based capillary flow channel. For the fabrication of a portable, automated and versatile sensor platform, we integrated a microcontroller, RF components, and a micropump for flow control. Calibration procedures ensured accurate measurements for both amplitude and phase, with a low drift rate (0.72 mdB/h and 1.00 mdeg./h, respectively) and high resolution (2.10 mdB and 6.10 mdeg.), indicating stable operation with minimal interface electronics. The capillary flow channel, implemented by confining the fluid on the sensing surface using a nitrocellulose strip, facilitated laminar and continuous sample flow with minimum damping of the acoustic signal. The sensor system was evaluated with two SAW devices at 100 and 200 MHz using glycerol dilutions within the range of 1% and 70%, demonstrating real-time monitoring capabilities and linear correlations between amplitude and phase changes. To prove the biosensing and clinical validity of the SAW newly developed system, DNA adsorption on a poly(L-lysine)-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) (PLL-g-PEG) functionalized SAW-surface was demonstrated with a detection limit of 0.001 μg/mL. Our study demonstrates the feasibility of a portable SAW sensor system coupled with a low-cost and replaceable capillary flow channel for real-time monitoring and biomolecular detection.
The full article can be accessed here.