Aug 25th 2015
Spanish Parliament starts to debate today the public budget for the next year. So that, we would like to review what are the plans to invest in research and innovation. According to the budget for the Secretary of Innovation, bioeconomy will be one of the priorities for the Spanish Government in 2016.
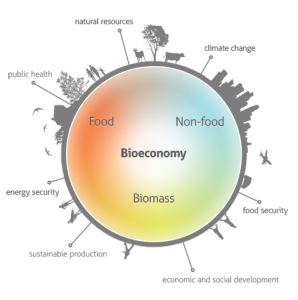
What is bioeconomy?
The bioeconomy definition according to the EFIB (European Forum for the Bioeconomy) is the following:
Bioeconomy encompasses the production of renewable biological resources and their conversion into food, feed, bio-based products and bioenergy via innovative and efficient technologies.
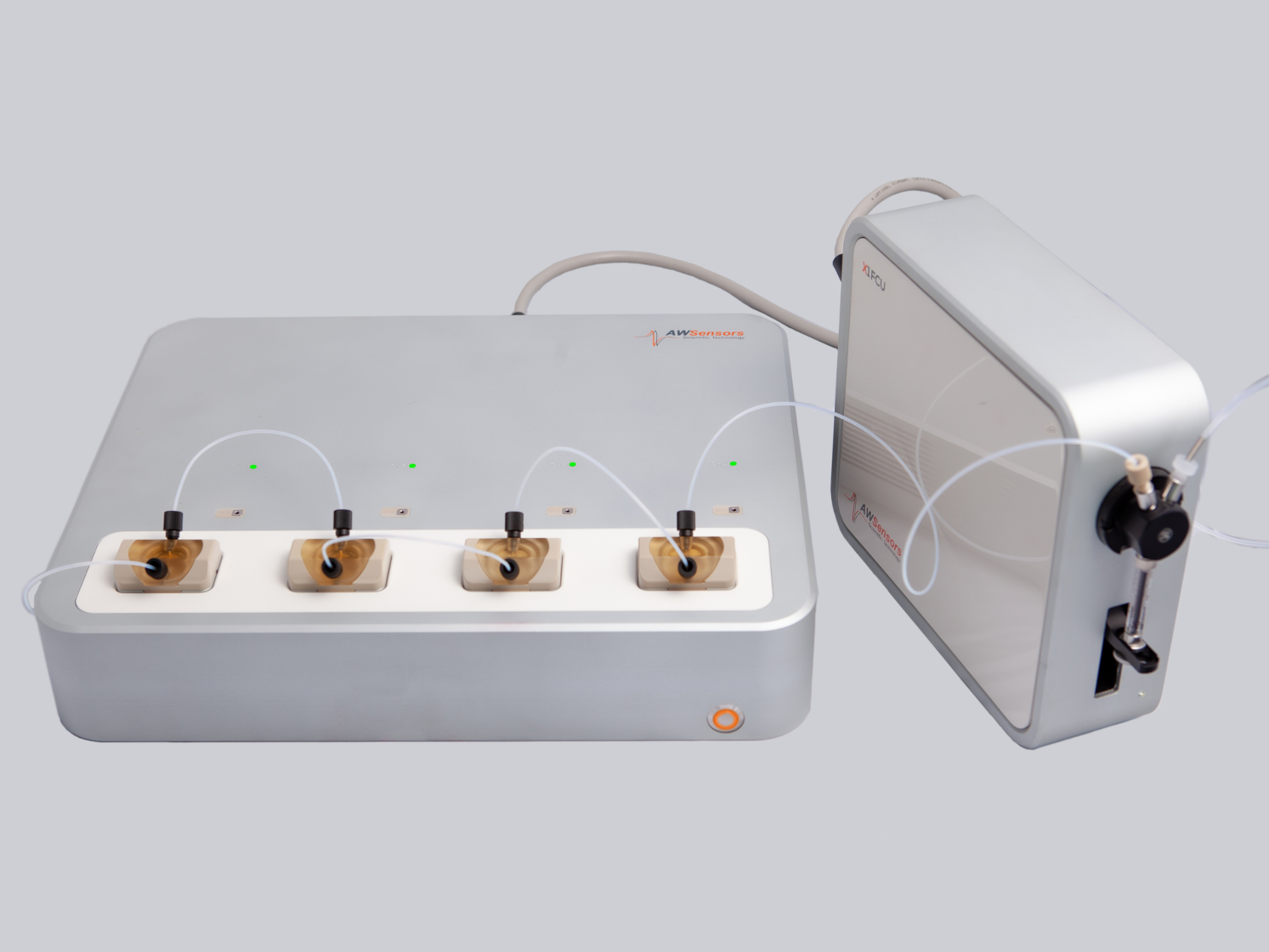
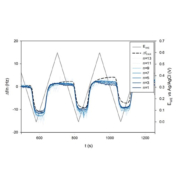
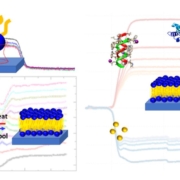
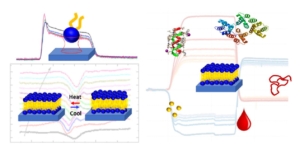
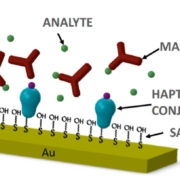
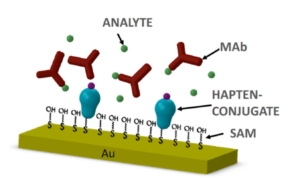
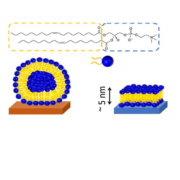
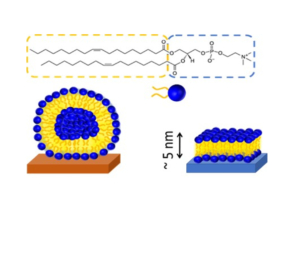
AWSensors tech has important applications in bioeconomy such as environmental monitoring, secure food and water, bioenergy or biomaterials. EU is promoting and funding projects in these fields in order to make the transition to a more resource efficient society and the Spanish Government is following this policy too.
Spain will boost the Bioeconomy Strategy in the public budget to research and development for 2016
Spanish government plans to invest 1,765 million euros in direct aid for innovation projects and 2,446 million euros for loans to enterprises. The resources allocated to direct aid will increase up to 15 per cent over this year and loans will decrease to 9 per cent. The government will give priority to areas considered most in need of development in science and technology such as Andalucia, Extremadura, Canarias, Castilla-La Mancha, Murcia, Galicia and Asturias. Among the actions to be undertaken in these regions, Bioeconomy will be boosted in the agri-food, biomass, bioenergy and bioproducts fields.
Furthermore, the Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI), the main driver of innovation in Spain, will have 30 million euros more for direct aid, 35.7% more than the previous year. The Spanish High Council Scientific Research (CSIC) will have 467 million euros next year and the Institute of Health Carlos III (ISCIII), 165 millions.
In spite of this state budget for 2016, Spain is still the 17th european country in gross domestic expenditure on R&D according to Eurostat.