AWSensors participa en el programa Becas E+E de IVACE
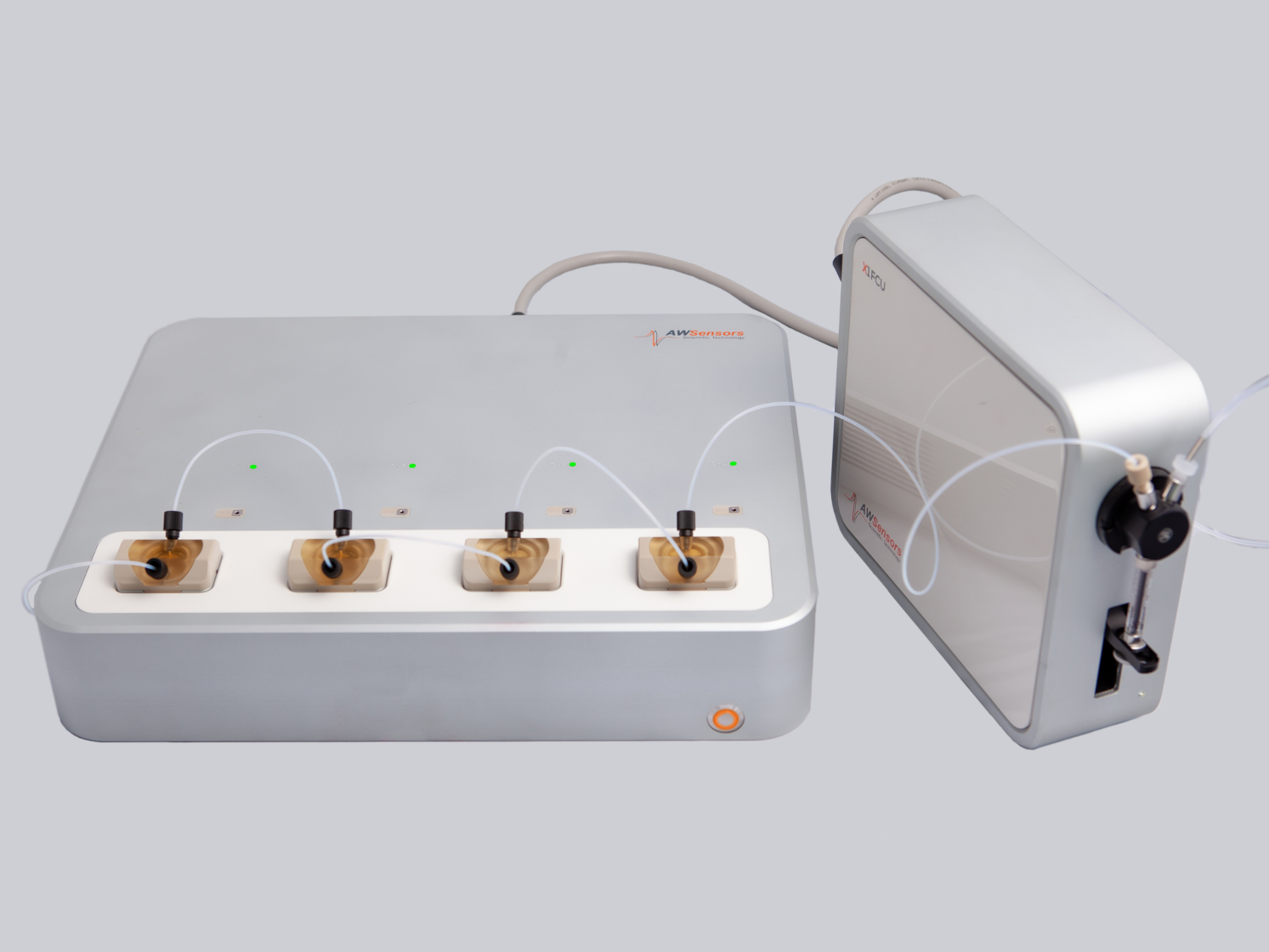
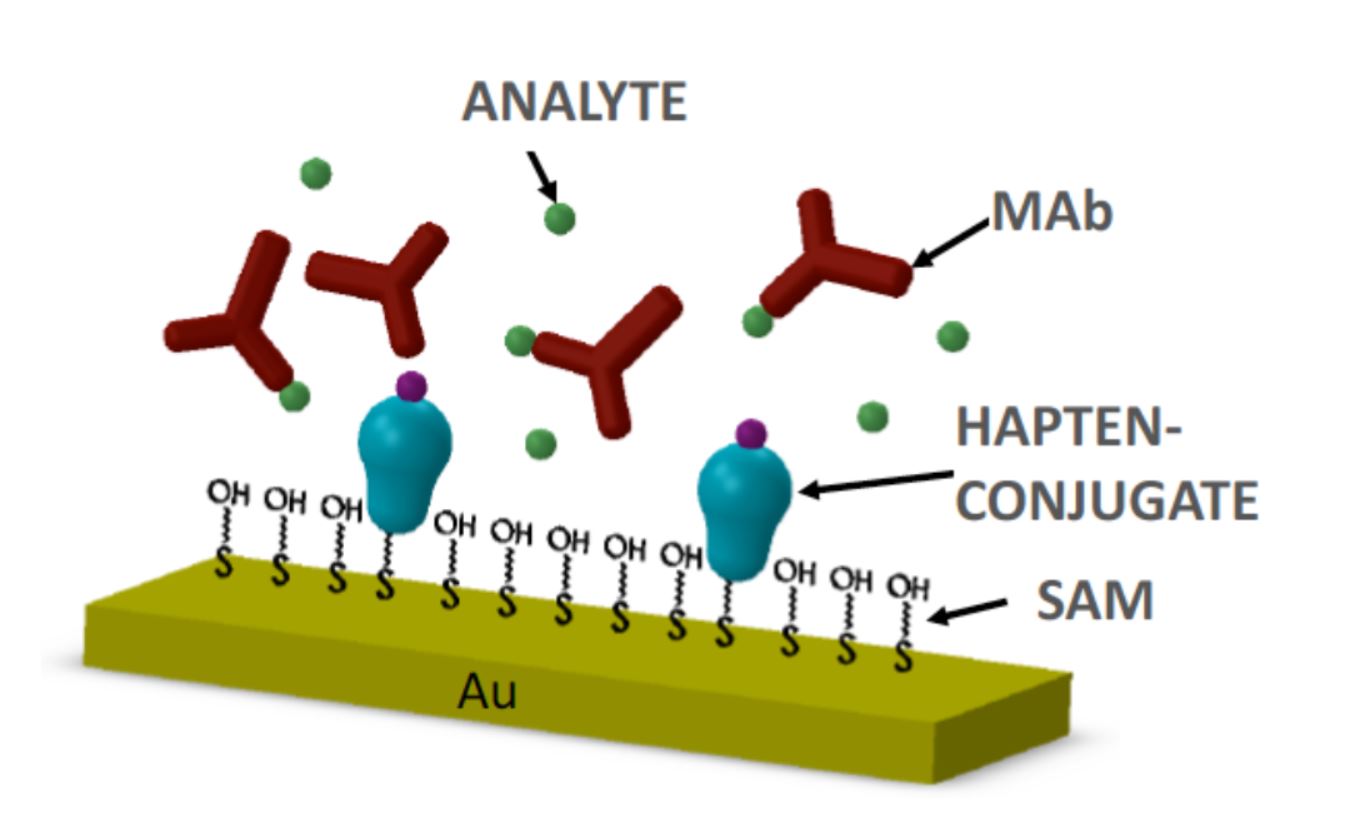
Siguiendo con la estrategia de internacionalización de AWSensors, la empresa incorpora a Nuria Portolés Cervera al equipo de Ventas y Marketing dentro del marco de su participación en el programa de Becas E+E – Exportación y Empleo 2021 del Instituto Valenciano de Competitividad Empresarial (IVACE). Durante 8 meses, Nuria cumplirá con un plan formativo en Comercio Exterior y contribuirá con su trabajo en la internacionalización y promoción de la marca y productos QCMD de AWSensors a nivel internacional.
El pasado 28 de diciembre de 2021 se otorgaron los destinos donde las personas becadas en este programa, como Nuria, realizan su formación práctica. Este acto institucional, que estuvo presidido por el Molt Honorable Sr. Ximo Puig, Presidente de la Generalitat Valenciana, y por el Conseller de Economía Sostenible, Sectores Productivos, Comercio y Trabajo, el Sr. Rafael Climent, tuvo lugar en el Palau de la Generalitat.

El programa de Becas E+E está gestionado por IVACE y financiado por el Fondo Social Europeo, dentro de la Iniciativa de empleo juvenil. El programa tiene por objetivo proporcionar una formación profesional en Comercio Exterior a las personas participantes, así como de dotar de más herramientas a las entidades y empresas participantes que sirvan de apoyo en su internacionalización.
![]()
Fuente: https://twitter.com/i/broadcasts/1OdKrBMzpneKX